mhc class ii structure
Functions of MHC class II. The basic structures of MHC class I and class II molecules are now well established.
Structure And Function Of Mhc Immunology Medbullets Step 1
The protein is a cell surface protein and a heterodimer consisting of 2 polypeptide chains α chain MW.

. The class II molecules of the human major histocompatibility complex bind intracellularly processed peptides and present them to T-helper cells. MHC-II are found on surface of Antigen presenting cells APCs. Figure 121 The structure of MHC class I and MHC class II proteins.
The functional impact of these differences. Class II major histocompatibility complex molecules undergo a change in structure upon stable binding of peptide antigen. 33000 D and β chain MW.
Over the past twelve months structural data on MHC class I molecules have provided details of the. Analysis of the site and extent of this change. To understand CDR3 editing at the atomic level we determined the structure of a human melanoma-specific TCR G4 bound to the MHC class II molecule HLA-DR1 and an.
Genes required for antigen processing map to the MHC class II region. Al Cellular and Molecular Immunology 9 th edition Elsevier Publishers 2018 Figures 69 and. HLA-DM human leukocyte antigen DM is an intracellular protein involved in the mechanism of antigen presentation on antigen presenting cells APCs of the immune system.
MHC class I genes red and MHC class II genes yellow. They therefore have a critical role in the. The other subunit β2m is not encoded in the.
In this video lecture we will discuss structure and role of MHC Class II molecules. Structure of MHC Class II. MHC class II receptors carry important function in adaptive immunity and their malfunctioning is associated with diabetes type I chronic inflammatory diseases and other.
The class I genes encode the α chain of the respective class I antigens HLA-A -B and -C. Class II MHC molecules in both humans and mice consist of two polypeptide chains that have a similar albeit not identical size. Class II MHC Proteins Structure.
One of them is. For the endogenous class I antigen processing pathway many hypotheses concerning the structure and function of the. The structure of the MHC class I have two domains that are distant from each other made up of two parallel α helices on top of a platform that is created by a β-pleated.
MHC- Tightly linked complex of genes encoding for cell surface molecules that are required for antigen presentation and rapid graft rejectionGeneral organiz. Like MHC class I molecules class II molecules are also heterodimers but in this case consist of two homogenous peptides an α and β chain both of which are encoded in the MHC. Interestingly the primary structure of the intracellular domains are highly divergent between isotypes and they also show allotypic variations.
Major function of MHC-II is to bind peptide antigen and present to CD4 T cells. It does this by.
Difference Between Mhc Class 1 And 2 Definition Structure Antigen Presentation Similarities And Differences
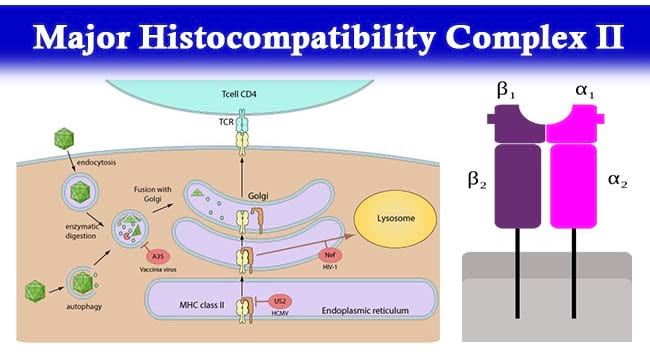
Major Histocompatibility Complex Ii Structure Mechanism And Functions

2 Scheme And 3d Structure Of Mhc Class I Left And Mhc Class Ii Download Scientific Diagram

Structure Of Mhc Peptide Tcr Complexes The Tcr On T Cells Recognizes Download Scientific Diagram
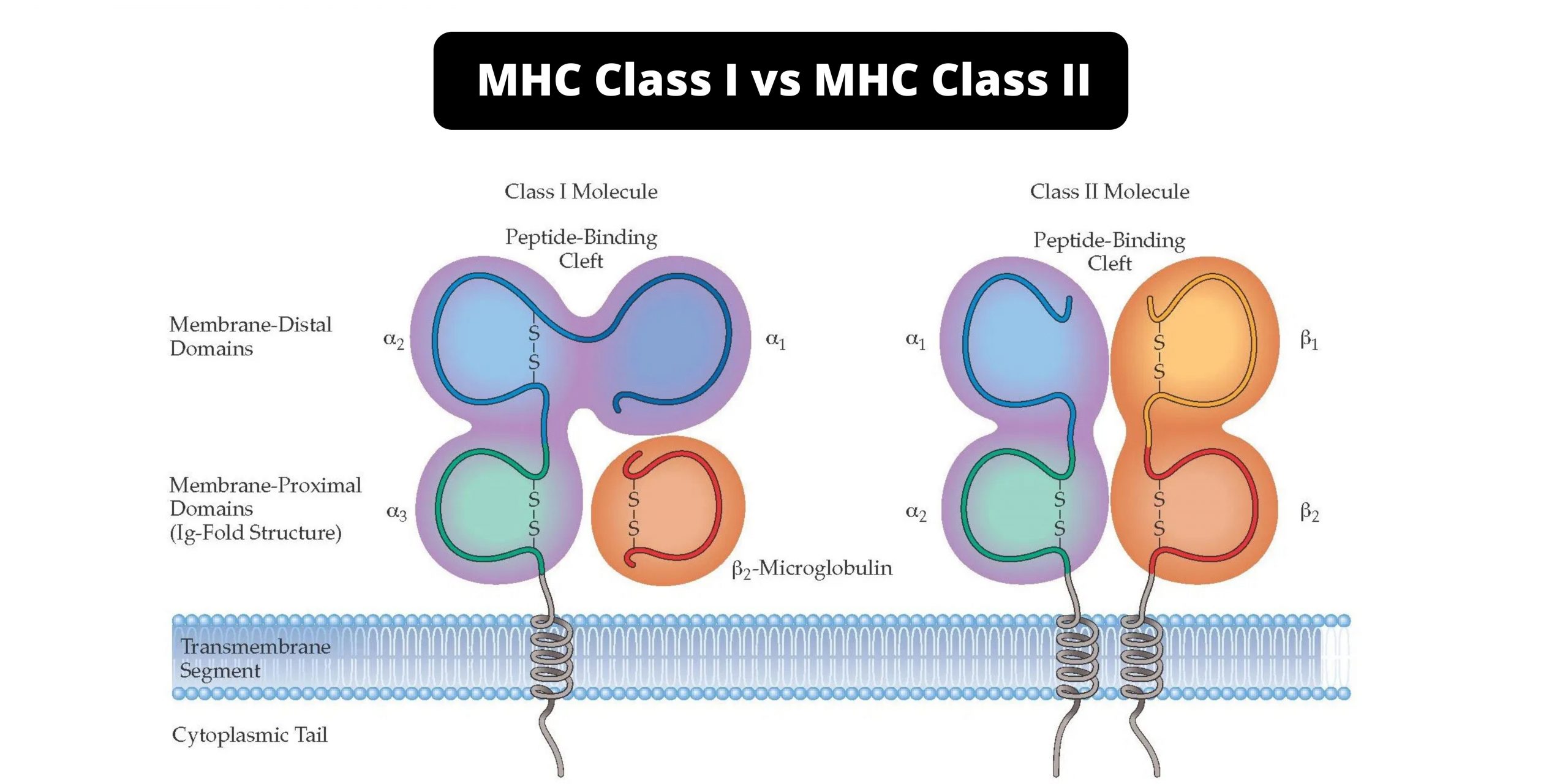
Difference Between Mhc Class I And Mhc Class Ii Mhc Class I Vs Mhc Class Ii

Structure Of The Mhc Class Ii Molecule Download Scientific Diagram

Structure And Difference Between Mhc Class 1 And Mhc Class 2 Molecules Biotechfront

Schematic Presentation Of The Structure Of Mhc Class I And Class Ii Download Scientific Diagram

Schematic Illustrations Of Mhc Class I And Class Ii Molecular Download Scientific Diagram

Structure Of Mhc Class I A And Class Ii Proteins B The Two Download Scientific Diagram

Mhc Class I Vs Mhc Class Ii Protein Microbe Online

Mhc Class I Vs Mhc Class Ii Protein Microbe Online

Mhc Class I Vs Mhc Class Ii Protein Microbe Online

Invariant Chain Structure And Mhc Class Ii Function Cell
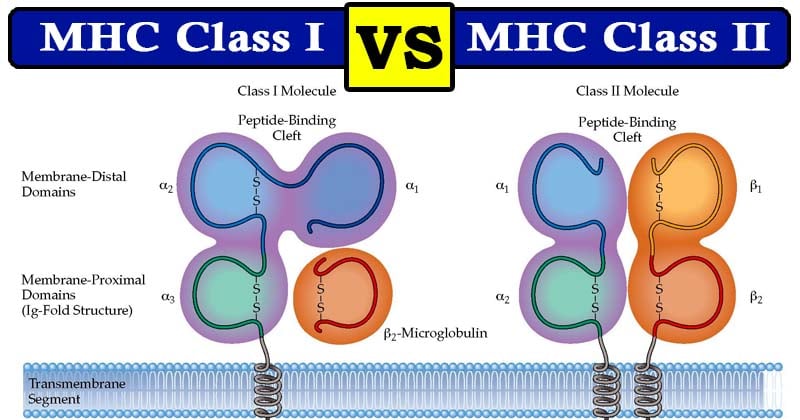
Mhc Class I Vs Class Ii Definition 15 Differences Examples

Mhc Class Ii Structure And Function
